| CPC H01J 9/12 (2013.01) [C01B 19/007 (2013.01); C23C 14/06 (2013.01); C23C 14/24 (2013.01); C23C 14/52 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
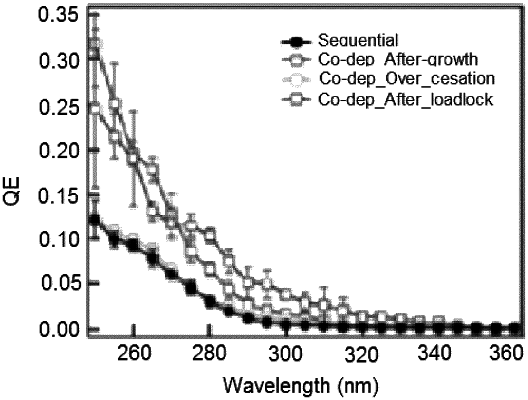
1. A method of growing photocathodes, comprising:
exposing a substrate of Si wafer to an alkali source comprising K and Li;
controlling co-evaporating growth and co-deposition; forming a growth including Te;
monitoring a stoichiometry of the growth, and forming the photocathodes having a 2 nm surface roughness and high quantum efficiency of 19% at 266 nm.
|