| CPC G16C 20/30 (2019.02) [G06F 30/20 (2020.01); G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06N 10/00 (2019.01); G16C 20/70 (2019.02)] | 21 Claims |
|
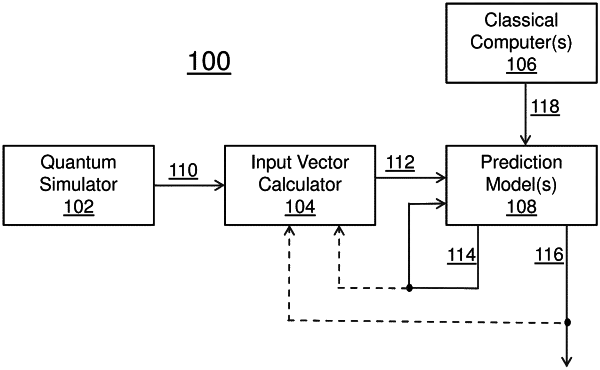
1. A method for predicting electronic structural information of a molecule, the method comprising:
generating quantum simulation results for the molecule based on a quantum simulation of an electronic structure of the molecule, wherein the quantum simulation of the electronic structure of the molecule is performed with one or more quantum processing units (QPUs);
creating an input vector comprising data field values derived from the quantum simulation results for the molecule; and
applying an electronic structural information prediction model to generate, based at least in part on the input vector, predicted electronic structural information for the molecule, wherein the electronic structural information prediction model is trained with training data instances corresponding to other types of molecules than said molecule, wherein a training data instance in the training data instances includes (a) a second quantum simulation result of a second electronic structure of a second molecule generated with a quantum computer and (b) a classical computing result of the second electronic structure of the second molecule generated with a classic computer.
|