| CPC G10L 25/21 (2013.01) [G10L 21/0232 (2013.01); H04R 3/04 (2013.01); G10L 2021/02082 (2013.01); G10L 2021/02163 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method for estimating a power spectral density of a signal component, the method comprising:
receiving, at one or more processing devices, an input signal representing audio captured using a microphone, the input signal comprising at least a first portion that represents acoustic output from a first audio source in an environment, and a second portion that represents other acoustic energy in the environment;
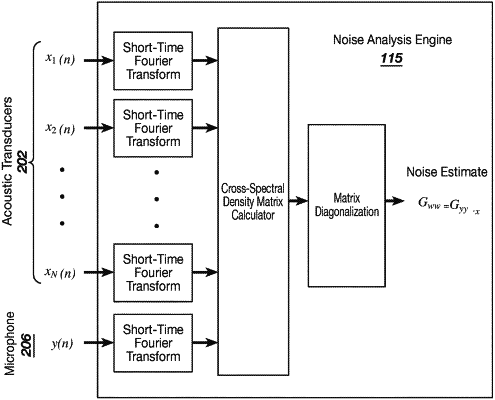
computing, by the one or more processing devices, a frequency domain representation of the input signal that includes a cross-spectral density matrix based on the input signal and an output of the first audio source;
iteratively modifying, by the one or more processing devices, the frequency domain representation of the input signal by a matrix diagonalization process on the cross-spectral density matrix, such that the modified frequency domain representation represents a portion of the input signal in which effects due to all but a selected one of the first and second portion is substantially reduced;
determining, from the modified frequency domain representation, an estimate of a power spectral density of the selected portion; and
at least one of reducing noise or echo in a microphone signal based upon the estimated power spectral density or inserting noise in a far end system based upon the estimated power spectral density.
|