| CPC G10L 21/02 (2013.01) | 20 Claims |
|
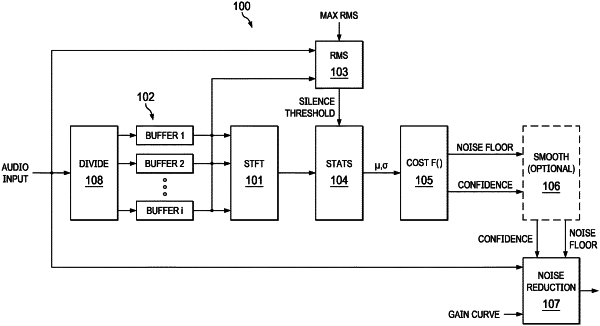
1. A method of estimating a noise floor of an audio signal, the method comprising:
obtaining, using one or more processors, the audio signal;
dividing, using the one or more processors, the audio signal into a plurality of buffers;
determining, using the one or more processors, time-frequency samples for each buffer of the audio signal;
for each buffer and for each frequency, determining, using the one or more processors, a median or mean and a measure of an amount of variation of energy based on the samples in the buffer and samples in neighboring buffers that together span a specified time range of the audio signal;
combining, using the one or more processors, the median or mean and the measure of the amount of variation into a cost function;
for each frequency:
determining, using the one or more processors, a signal energy of a particular buffer of the audio signal that corresponds to a minimum value of the cost function;
selecting, using the one or more processors, the signal energy as the estimated noise floor of the audio signal; and
reducing, using the one or more processors and the estimated noise floor, noise in the audio signal.
|