| CPC G06N 3/067 (2013.01) [G06F 17/16 (2013.01); G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
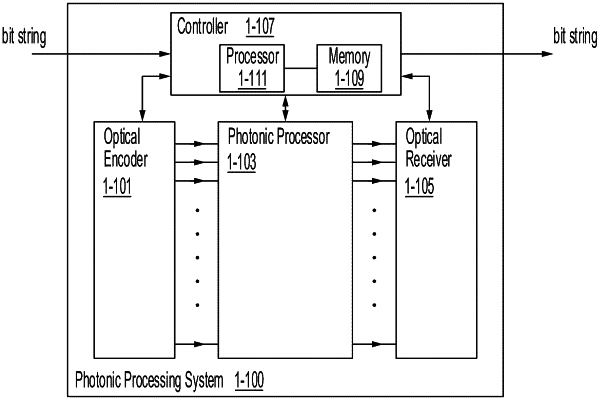
|
1. A method performed by a photonic processing system, the method comprising:
pre-processing at least one input signal and/or at least one filter signal by expanding and/or flattening the at least one input signal and/or the at least one filter signal;
computing, using the photonic processing system, at least one of a convolution and a cross-correlation on the at least one input signal and the at least one filter signal by performing a matrix multiplication operation, wherein:
the at least one input signal and at least one filter signal are at least one dimensional and comprise at least one data channel; and
the at least one convolution and cross-correlation produce an at least one output signal that is at least one dimensional and comprises at least one data channel; and
post-processing the at least one output signal by rotating vector rows of a matrix forming the at least one output signal, the rotating comprising shifting matrix element positions within the vector rows.
|