| CPC G06F 21/56 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0622 (2013.01); G06F 3/0659 (2013.01); G06F 3/0673 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
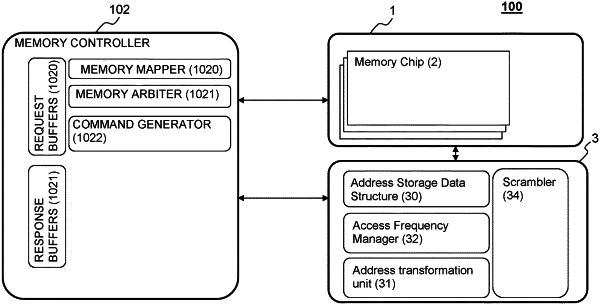
1. A memory device comprising a memory comprising at least one chip, each chip comprising one or more banks for storing a plurality of bits, each bank comprising a set of rows and columns, each row and column comprising a number of bits, the memory device further comprising a controller configured to generate access commands to the memory, an access command identifying an address corresponding to a given row of the memory and a command operation to be performed on said given row, wherein the memory device further comprises a protection device, said protection device comprising:
a transformation unit configured to apply a transformation function in response to a receipt of an access command identifying an address, to transform said address into a transformed address, wherein said transformation function is a balanced and non-injective transformation function;
an address storage data structure configured to store the transformed address depending on a frequency of access associated with said address, said address storage data structure being reset in response to a memory protection operation performed in the memory device; and
the protection device further comprising an access frequency manager configured to determine whether an access frequency associated with an address maintained in the address storage data structure is greater or equal to a threshold, and if so trigger a memory protection operation in the memory from within the memory, wherein the access frequency manager comprises an access counter configured to count the accesses to said address between two memory protection operations of the memory, which provides a counter value, the access frequency associated with said address being determined using said counter value, wherein said memory protection operation is a refresh operation.
|