| CPC G06F 11/3457 (2013.01) [G06F 11/302 (2013.01); G06F 11/3086 (2013.01); G06N 5/045 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
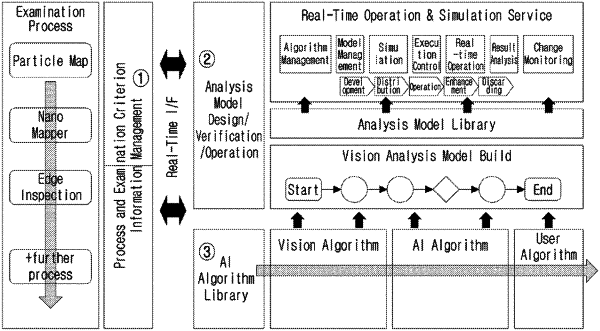
1. An explainable artificial intelligence (AI) modeling and simulation method comprising the steps of:
when an algorithm suitable for a workflow created and edited according to a subject area is selected from pre-stored algorithms, designing an AI workflow model; and
when input information is inputted, performing a simulation for an AI workflow model with respect to the input information,
wherein the step of performing the simulation comprises:
a step of, when a plurality of deep learning AI workflow models or a plurality of machine learning AI workflow models are designed, registering a simulation for each AI workflow model; and
a step of performing the registered respective simulations,
wherein the method further comprises:
a step of, when the respective simulations are performed, comparing and evaluating performance of the respective AI workflow models in real time based on results of performing the respective simulations; and
a step of continuously distributing or changing an optimal AI workflow model according to a result of comparing and evaluating in real time,
wherein the step of performing the registered respective simulations comprises:
a step of, when image data is inputted, dividing the image data into analysis unit areas, determining whether there is a defect in each area, and determining a grade according to a result of determining;
a step of extracting image features by measuring an area of interest which is determined as having a defect;
a step of searching similar images of the image features;
a step of estimating a fault-causing factor by analyzing commonality of the similar images; and
a step of generating explanation data including the fault-causing factor.
|