| CPC G02B 15/22 (2013.01) [G02B 27/0025 (2013.01); G03B 7/091 (2013.01); G02B 13/009 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
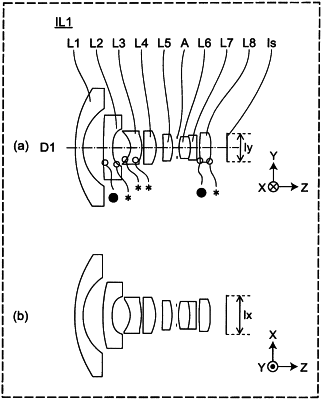
1. An imaging optical system having an image circle defined on an imaging element, the imaging optical system comprising:
lens elements arranged from an object side to an image plane side; and
a diaphragm arranged between two of the lens elements that are adjacent to each other,
wherein:
the lens elements include freeform lens elements, each having a freeform surface that is an asymmetrical surface with respect to a first cross section and a second cross section, the first cross section being defined by a first direction and an optical axis direction, the second cross section being defined by a second direction and the optical axis direction, the first direction crossing the second direction, and the optical axis direction being orthogonal to the first direction and the second direction;
at least two of the freeform lens elements are located on an object side of the diaphragm;
the image circle has a first diameter in the first direction and a second diameter in the second direction, the first diameter being equal to or larger than the second diameter;
the imaging optical system satisfies a following conditional expression (1) based on a summation for the freeform surfaces of the at least two of the freeform lens elements located on the object side of the diaphragm:
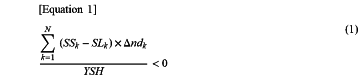 N is a total number of the freeform surfaces of the at least two of the freeform lens elements located on the object side of the diaphragm;
k is a number identifying a k-th freeform surface of the total number of the freeform surfaces of the at least two of the freeform lens elements located on the object side of the diaphragm;
SLk is a sag amount at a first position where a first height of the k-th freeform surface in the first direction is 50% of a shortest image height among the image circle;
SSk is a sag amount at a second position where a second height of the k-th freeform surface in the second direction is 50% of the shortest image height among the image circle;
Δndk is a difference resulting from subtracting a refractive index on an object side of the k-th freeform surface from a refractive index on an image plane side of the k-th freeform surface; and
YSH is a height of 50% of the shortest image height among the image circle.
|