| CPC G02B 1/12 (2013.01) [C03C 17/22 (2013.01); C03C 17/245 (2013.01); C03C 17/2453 (2013.01); C03C 17/34 (2013.01); C03C 17/3417 (2013.01); C23C 14/081 (2013.01); C23C 14/086 (2013.01); C23C 16/403 (2013.01); C23C 16/407 (2013.01); C23C 16/45557 (2013.01); H01B 1/00 (2013.01); H10K 71/60 (2023.02); C03C 2217/231 (2013.01); C03C 2217/948 (2013.01); C03C 2218/156 (2013.01); C03C 2218/32 (2013.01); C03C 2218/34 (2013.01); H10K 77/10 (2023.02); H10K 2102/103 (2023.02)] | 9 Claims |
|
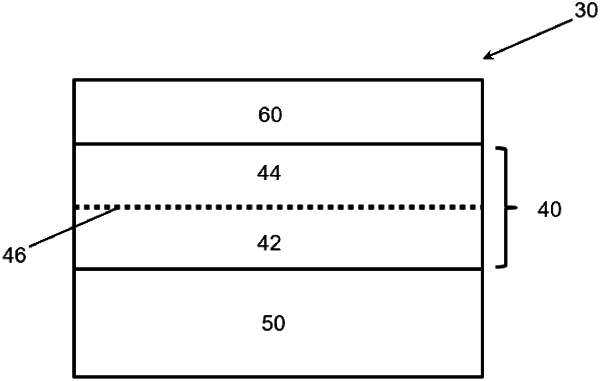
1. A method of producing a coated glass substrate comprising a layer comprising a transparent conductive oxide, comprising:
a. vacuum depositing over at least a portion of a substrate in an inert atmosphere comprising oxygen within a range of from 0 to 2.5%, an oxygen-deficient sub-stoichiometric transparent metal oxide layer having an absorption coefficient at a wavelength in the visible spectrum of at least 1,000 cm−1, wherein the oxygen-deficient sub-stoichiometric transparent metal oxide layer comprises a transparent conductive oxide comprising indium tin oxide; and
b. annealing at least a portion of the oxygen-deficient sub-stoichiometric transparent metal oxide layer by flashing at least a portion of the transparent conductive oxide layer at a temperature ranging from 15° C. to 40° C., with a pulse energy ranging from 3.5 J/cm2 to 6.0 J/cm2, of non-coherent light within the visible spectrum including light at a wavelength at which the layer has an absorption coefficient of at least 1,000 cm−1,
wherein the pulse of non-coherent light has a voltage of at least 500 V and up to 540 V and a pulse length of 2,000 μs, or wherein the pulse of non-coherent light has a voltage of greater than 540 V and less than 600 V and a pulse length of 1,000 μs, or wherein the pulse of non-coherent light has a voltage of at least 600 V and less than 650 V and a pulse length of 500 μs, or wherein the pulse of non-coherent light has a voltage of at least 650 V and less than 700 V and a pulse length of 400 μs, or wherein the pulse of non-coherent light has a voltage of at least 700 V and up to 730 V and a pulse length of 300 μs, and
wherein the pulse has a penetration depth in the transparent metal oxide layer that is less than the thickness of the layer producing a split layer of the portion of the transparent conductive oxide layer, where each layer of the split layer has a different physical property.
|