| CPC G01N 15/1433 (2024.01) [G01B 9/02097 (2013.01); G01N 15/1434 (2013.01); G01N 2015/1454 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
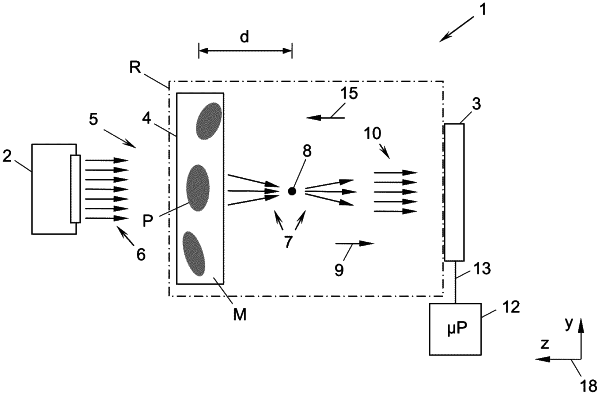
1. A method for determining a focal length of a transparent particle in a medium, comprising:
providing a sample of the medium containing said particle;
emitting, with a light source, a coherent light beam to irradiate the sample, wherein a first part of the light beam is scattered by the particle to create a scattered light beam which has a focus in a beam direction behind or in front of the particle;
recording, with a camera, an interference image of the scattered light beam and a second part of the light beam that has not been scattered by the particle-;
computing, with a processor, for each one of a set of positions which are three-dimensionally distributed in a space including the particle and the focus, an electric field of the first part of the light beam from the interference image;
generating, with the processor, a representation of the light beam covering said positions, and comprising, for each of said positions, an intensity value of the coherent light beam calculated from the computed electric field at that position;
finding, with the processor, two positions, a first of which lies in the sample, a second of which lies in the beam direction behind or in front of said first position, and the intensity value for each of which positions is greater than the respective intensity values for nearby positions; and
determining, with the processor, the focal length from the two found positions;
wherein, in the step of generating, for each position, the intensity value is calculated according to
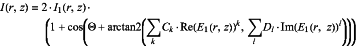 with
r, z being coordinates of the position, wherein z is a coordinate in an opposite direction to the beam direction and r denotes a pair of coordinates in a plane x, y perpendicular to said opposite direction,
I(r,z) being the intensity value for the position,
I1(r,z) being an intensity of the first part of the light beam for the position,
Θ being a phase shift parameter,
k, l being indices of summation,
Ck, Dl being expansion parameters,
E1(r,z) being the computed electric field for the position, and
arctan 2 denoting a four quadrant inverse tangent function.
|