| CPC B60W 50/0098 (2013.01) [B66F 9/063 (2013.01); G01S 17/89 (2013.01); G05B 11/36 (2013.01); G05B 13/048 (2013.01); G05D 1/0212 (2013.01); G05D 1/0248 (2013.01); B60W 2050/0011 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
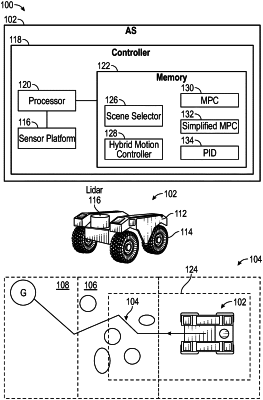
determining, based on output of a sensor platform, crowding of a space around an automated system, wherein the automated system comprises a battery, and wherein the crowding is determined by comparing a number of objects in the space and a narrowness of the space to a threshold;
selecting, based on the space being crowded, a model predictive control scheme to navigate the automated system to a goal;
determining, during navigation, real-time computational overrun by the automated system;
selecting, based on the computational overrun to navigate the automated system to the goal, a simplified model predictive control scheme in order to ensure real-time running of the automated system;
selecting, based on the space being open and the goal being within the space, a proportional-integral-derivative scheme;
switching among each of the model predictive control scheme, the simplified model predictive control scheme, and the proportional-integral-derivative scheme in order to conserve energy of the battery while also achieving a predetermined desired motion performance in real-time operation; and
autonomously moving the automated system to the goal with the proportional-integral-derivative scheme selected,
wherein the simplified model predictive control scheme assumes a constant velocity of the automated system during trajectory prediction, and wherein the simplified model predictive control scheme is utilized to determine a discrete control space instead of a continuous control space,
wherein power consumption by the automated system is reduced by switching to the simplified model predictive control scheme, and
wherein the crowding is further determined by tracking legs of people at the space.
|