| CPC B22D 11/114 (2013.01) [B22D 11/001 (2013.01); B22D 11/0611 (2013.01); B22D 11/0642 (2013.01); B22D 11/0651 (2013.01); H01F 1/14775 (2013.01); H01F 1/15341 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method for improving the core loss properties of an amorphous foil produced by Planar-Flow Melt Spinning (PFMS), the method comprising:
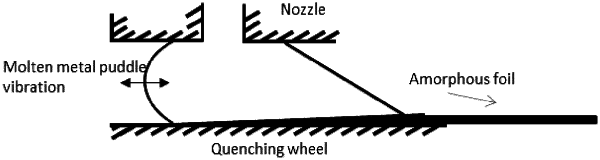
mechanically scribing the amorphous foil, having a width of 75 to 260 mm, spaced at controlled wavelengths by controlling a capillary vibration in a molten metal puddle that forms between a crucible nozzle and a quenching wheel at a controlled frequency such that a uniform scribing pattern is formed continuously across the width of the amorphous foil, by:
maintaining a gap height between the nozzle and the quench wheel constant across the width of the foil such that the scribed pattern on the amorphous foil is spaced at controlled wavelengths, wherein the frequency of the capillary vibration is represented by f˜(σ/ρ*G3)1/2, where ρ is a density of the molten metal, G is the gap height, and σ is surface tension of the molten metal, and the frequency of the capillary vibration is dependent on the gap height, and
contouring the shape of the nozzle to accommodate the thermal deformations of the quench wheel,
wherein the scribing is applied in-line while the amorphous foil is being cast.
|