| CPC A61K 31/405 (2013.01) [A61K 31/404 (2013.01); A61P 33/02 (2018.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method of treating a protozoan infection, the method comprising: administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically-effective amount of a compound of the formula:
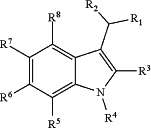 wherein:
R1 is —CN, —C(═O)NHOH, or —C(═O)NH2;
R2 is substituted or unsubstituted phenyl;
R3 is methyl, phenyl, naphthalen-1-yl, or naphthalen-2-yl;
R4 is methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl, or hydrogen; and
each R5, R6, R7, and R8 is hydrogen,
or a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt thereof.
|