| CPC A61B 5/14532 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/4842 (2013.01); A61B 5/4848 (2013.01); A61B 5/4866 (2013.01); G01N 21/35 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
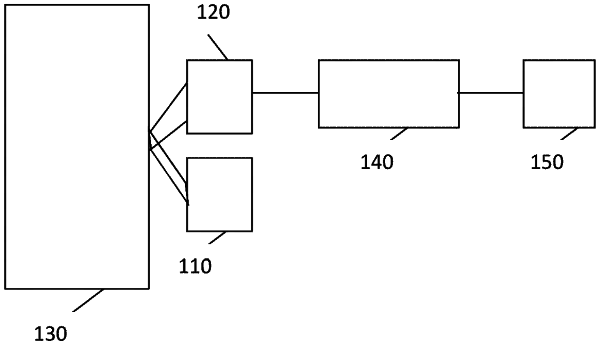
|
1. A method for measuring post-translational modification of proteins in a subject, the method comprising:
measuring and recording of infrared radiation within a predetermined wavenumber range on a nail plate of the subject, wherein said nail plate is still attached to said subject, the infrared radiation being attenuated by nail plate protein glycation in the nail plate;
comparing said attenuation of infrared radiation to a predetermined value for deriving information regarding post-translational modification of proteins in the nail plate;
wherein said comparing comprises comparing a contribution of different spectral bands within a range of 4000 cm−1 to 4500 cm−1; and
deriving a degree of glycemia in the subject based on said comparison of the contribution of different spectral bands within the range of 4000 cm−1 to 4500 cm−1,
wherein said attenuation of infrared radiation comprises attenuation by post-translational modified integument protein in said nail, said protein being a keratin.
|