| CPC A61B 5/0066 (2013.01) [A61B 5/055 (2013.01); A61B 5/7425 (2013.01); A61B 34/20 (2016.02); A61B 90/37 (2016.02); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G16H 20/40 (2018.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); A61B 5/0095 (2013.01); A61B 2034/2065 (2016.02); A61B 2090/3735 (2016.02); A61B 2090/374 (2016.02); G06T 2207/10088 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10101 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method of tracking positions of surgical imaging devices by way of a computing device comprising a processor, the method comprising:
by using the processor,
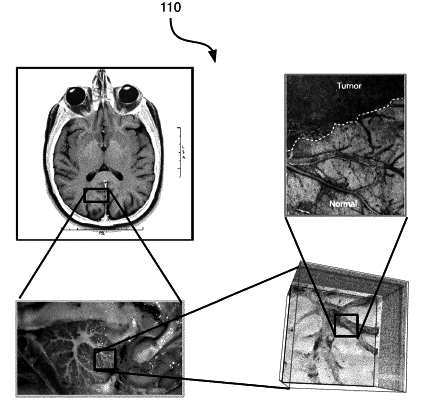
receiving a first intraoperative image of a first area of a patient from a first imaging device, the first intraoperative image having a first intraoperative image resolution finer than a preoperative image resolution of a preoperative image;
receiving a position of the first imaging device in a coordinate system from an optical tracking system;
receiving a second intraoperative image of a second area of the patient from a second imaging device, the second intraoperative image depicting the second area within the first area, and the second intraoperative image having a second intraoperative image resolution finer than first intraoperative image resolution;
registering a second intraoperative image with the first intraoperative image, thereby providing a registration of the second intraoperative image with the first intraoperative image;
determining a position of a second imaging device in the coordinate system based on the registration of the second intraoperative image with the first intraoperative image;
determining whether a subsequent imaging device is detected, and
when the subsequent imaging device is detected,
receiving a subsequent intraoperative image of a subsequent area of the patient from the subsequent imaging device, the subsequent intraoperative image depicting the subsequent area within a previous area, and the subsequent intraoperative image having a subsequent intraoperative image resolution finer than that of a previous intraoperative image resolution;
registering the subsequent intraoperative image with a previous intraoperative image, thereby providing a registration of the subsequent intraoperative image with the previous intraoperative image; and
determining a position of the subsequent imaging device in the coordinate system based on the registration of the subsequent intraoperative image with the previous intraoperative image; and
controlling a display to present the preoperative image overlaid with the first intraoperative image, the first intraoperative image overlaid with second intraoperative image, based on the position of the second imaging device,
the previous intraoperative image overlaid with the subsequent intraoperative image, and
each of the first intraoperative image and the second intraoperative image related to a distinct imaging modality.
|