| CPC A61B 18/1492 (2013.01) [A61B 2017/22067 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22079 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00083 (2013.01); A61B 2018/0041 (2013.01); A61B 2018/1435 (2013.01); A61B 2018/144 (2013.01); A61B 2218/007 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
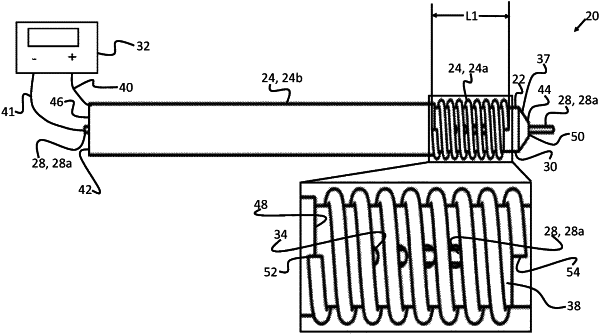
1. An apparatus for removal of a thrombus from a body of a subject, the apparatus comprising:
an electrically-insulating tube, which comprises a distal end having a circumferential wall that is shaped to define multiple perforations along a length of the distal end, configured for insertion into the body of the subject;
an outer electrode wrapped around the distal end of the electrically-insulating tube from a first location proximal to a proximalmost one of the multiple perforations to a second location distal to a distalmost one of the multiple perforations, and configured to lie at least partly within the thrombus while the electrically-insulating tube is inside the body of the subject; and
an inner electrode, configured to lie, within the electrically-insulating tube, opposite the multiple perforations such that the inner electrode is radially separated from the outer electrode, while the outer electrode lies at least partly within the thrombus,
the outer electrode being configured to attract the thrombus while the outer electrode lies at least partly within the thrombus and the inner electrode lies opposite the multiple perforations when a positive voltage is applied between the outer electrode and the inner electrode such that an electric current flows through the multiple perforations.
|