| CPC A61B 18/1492 (2013.01) [A61B 18/18 (2013.01); A61B 5/287 (2021.01); A61B 5/361 (2021.01); A61B 5/364 (2021.01); A61B 5/4848 (2013.01); A61B 8/12 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00154 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00221 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00077 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00095 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00101 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00351 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00577 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00642 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00708 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00791 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00797 (2013.01); A61B 2018/00839 (2013.01); A61B 18/24 (2013.01); A61B 2218/002 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
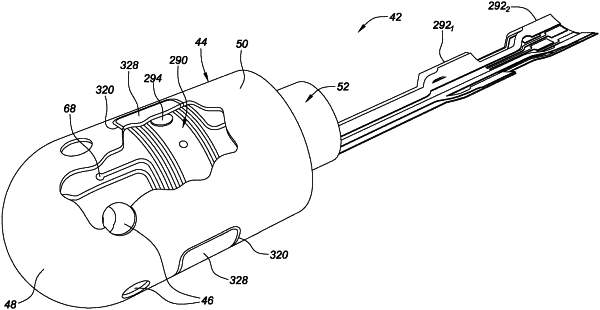
1. An ablation catheter tip, the tip comprising:
an electrically-conductive housing comprising a conductive shell including a domed distal end and a cylindrical body;
a thermally-insulative tip insert, wherein the conductive shell surrounds at least a portion of the thermally-insulative tip insert; and
a flexible electronic circuit distributed around the thermally-insulative tip insert, and comprising:
a top layer comprising copper, an intermediate polyimide layer, and a bottom layer comprising constantan disposed opposite the top layer;
a plurality of thermal sensors in thermal communication with the conductive shell and configured to provide directional temperature feedback, wherein the plurality of thermal sensors is distributed in two circumferential rings around the cylindrical body, wherein the first circumferential ring is longitudinally offset relative to the second circumferential ring; and
a wired or wireless communication pathway at least partially disposed on the flexible electronic circuit, communicatively connected to the plurality of thermal sensors, and configured to report the directional temperature feedback to an ablation control system;
wherein the ablation control system is configured to supply radio frequency (RF) energy to the electrically-conductive housing, and pulse the RF energy based on the directional temperature feedback and a temperature setpoint;
wherein the two circumferential rings do not extend onto the domed distal end of the conductive shell; and
wherein each of the plurality of thermal sensors is formed by an electrical via extending through the top layer, the intermediate polyimide layer, and the bottom layer.
|