| CPC H03M 13/136 (2013.01) [G06N 10/00 (2019.01); H03M 13/353 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
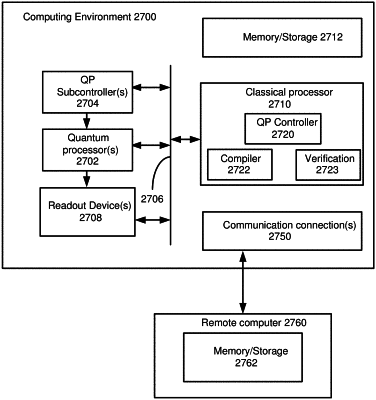
|
1. One or more computer-readable media storing computer-readable instructions, which when executed by a classical computer, cause the classical computer to perform a method, the method comprising:
determining a set of residual errors associated with an observed syndrome;
performing a sequence of operations until all residual errors in the determined set of residual errors are eliminated, the sequence including:
generating a set of random vectors, each one of the random vectors being a parity measurement of one or more stabilizers defined for a linear code;
adding a select one of the random vectors to a solution set, the select one of the random vectors having a largest detection power of the set of random vectors; and
updating the set of residual errors to eliminate a subset of the residual errors that are detectable by the select one of the random vectors to generate a fault-tolerant error-correction scheme; and
causing the fault-tolerant error-correction scheme to be generated in a plurality of qubits of a quantum computing device.
|