| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G06N 3/084 (2013.01); G06T 3/4007 (2013.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
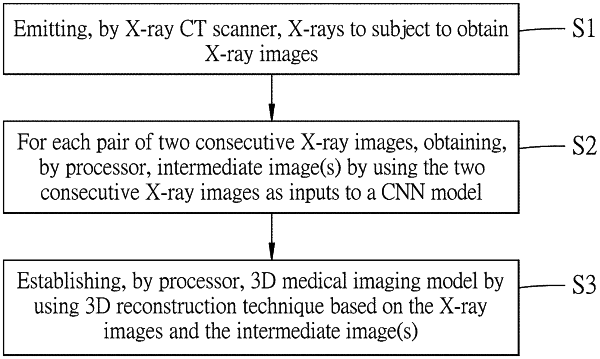
1. A method for establishing a three-dimensional medical imaging model of a subject, to be implemented by an X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner and a processor, the method comprising:
emitting, by the X-ray CT scanner, X-rays on the subject sequentially from plural angles with respect to the subject so as to obtain M number of X-ray images of the subject in sequence, where M is a positive integer greater than one;
for each pair of consecutive X-ray images among the M number of X-ray images, obtaining, by the processor, at least one intermediate image by using the pair of consecutive X-ray images as inputs to a convolutional neural network (CNN) model that has been trained for frame interpolation; and
establishing, by the processor, the three-dimensional medical imaging model of the subject by using a three-dimensional reconstruction technique based on the M number of X-ray images and the intermediate images that are obtained for the M number of X-ray images, wherein for each pair of consecutive X-ray images, the corresponding at least one intermediate image is to be interpolated between the consecutive input images of the pair,
prior to obtaining the at least one intermediate image, the method further comprising:
training the CNN model by using N number of additional X-ray images, where N is a positive integer and is equal to M+(M−1)×K, where K is a number of the at least one intermediate image for each pair of consecutive X-ray images.
|