| CPC G06F 1/3287 (2013.01) [G06F 1/3237 (2013.01); G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06N 3/063 (2013.01); G06V 20/56 (2022.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
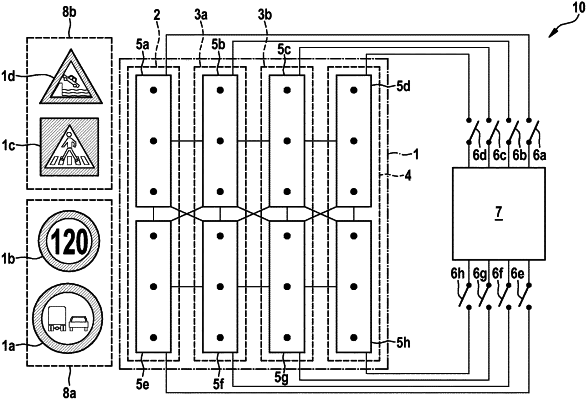
1. A hardware architecture for an artificial neural network (ANN), the ANN including a consecutive series of layers, each of the layers mapping its input variables onto output variables, and each of the output variables of the layers being input variables of a particular layer that follows in the series, the hardware architecture comprising:
a plurality of processing units, an implementation of each of the layers being split among at least two of the processing units; and
at least one resettable switch-off device that is configured to selectively deactivate at least one of the processing units, independently of the input variables supplied to the at least one of the processing units, so that at least one further one of the processing units remains activated in all layers of the consecutive series of layers whose implementation is contributed to by the at least one of the processing units, wherein:
the layers map the input variables onto the output variables using a plurality of neurons, in the split of the implementation, computation of the plurality of neurons being split among at least two of the processing units,
at least one of the at least two of the processing units has a share in the implementation of multiple layers of the consecutive layers, and
by selectively deactivating the at least one of the processing units, the resettable switch-off device deactivates a subset of the plurality of neurons associated with the at least one of the processing units.
|