| CPC C22B 34/34 (2013.01) [B03D 1/002 (2013.01); C22B 3/22 (2013.01); C22B 15/0084 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
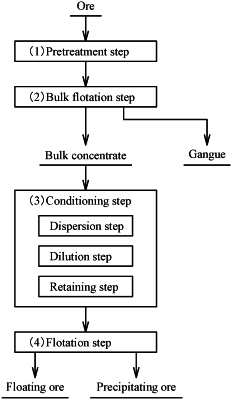
1. A mineral processing method, comprising:
a conditioning step of adding sulfite as a surface treatment agent to a mineral slurry containing a copper mineral and a molybdenum mineral; and
a flotation step of performing flotation which separates the molybdenum mineral as a floating ore and the copper mineral as a precipitating ore of the mineral slurry after the conditioning step,
wherein the conditioning step comprises adding a pH adjusting agent to adjust the pH of the liquid phase of the mineral slurry to range from 8 to 11.5;
wherein the sulfite is sodium hydrogen sulfite; and
wherein in the conditioning step, the sodium hydrogen sulfite is added at 0.10 mol/L to 0.25 mol/L in the liquid phase of the slurry.
|