| CPC A61K 49/10 (2013.01) [A61K 51/04 (2013.01); C07C 251/76 (2013.01); C07C 309/46 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method of detecting a freely diffusing small molecule aldehyde in a subject comprising administering an aldehyde-binding compound of Formula I to the subject and detecting the product of the compound of Formula I and the freely diffusing small molecule aldehyde using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), CEST-MRI or positron emission tomography (PET) imaging;
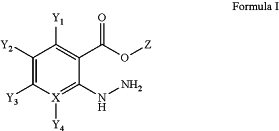 wherein:
X is C or N;
Z is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl;
Y1 and Y3 are H;
Y2 is CHs3—O—; and
Y4 is independently:
H;
a substituent selected from the group consisting of Br, CI, I, nitro, sulfo, carboxy, hydroxyl, alkoxy, cycloalkoxy, aryloxy, C1-6 alkyl, aryl, cycloalkyl, alkyne, propargyl, and tetrazine;
wherein detection of said freely diffusing small molecule aldehyde is indicative of a brain injury or of cell death optionally wherein the aldehyde-binding compound additionally comprises a radio-label for use in positron emission tomography imaging.
|