| CPC H04L 45/125 (2013.01) [H04L 45/123 (2013.01); H04L 45/302 (2013.01); H04L 47/122 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
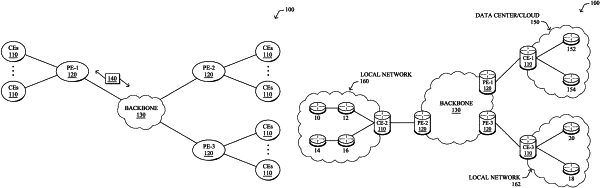
1. A method comprising:
predicting, by a device and for each of a plurality of applications accessible via a network, quality metrics for different paths in the network, wherein traffic for each of the plurality of applications may be routed via one or more paths among the different paths in the network, wherein the quality metrics comprise Quality of Experience metrics indicative of user application experience for each of the plurality of applications;
generating, by the device, a congestion risk prediction model that predicts a risk of traffic congestion for a particular combination of: applications from among the plurality of applications, traffic flows associated with those applications, and paths among the different paths in the network via which those traffic flows may be routed;
performing, by the device, a constrained optimization based on the quality metrics predicted for the different paths and on the risk of traffic congestion predicted by the congestion risk prediction model, to assign traffic flows associated with the plurality of applications to a selected subset of the different paths; and
causing, by the device, the traffic flows associated with the plurality of applications to be routed in the network via the selected subset of the different paths to which they are assigned.
|