| CPC H04L 45/122 (2013.01) [H04L 45/02 (2013.01); H04L 47/122 (2013.01); H04L 47/22 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
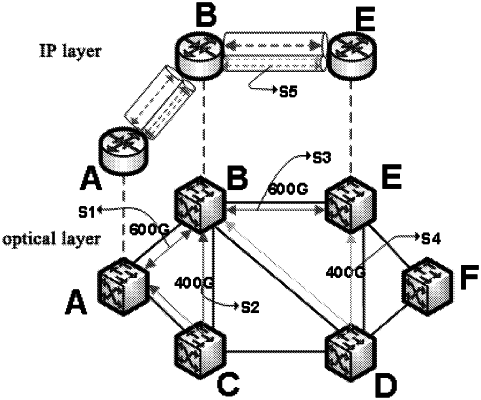
1. A method for load-balanced traffic grooming in an IP over “Quasi-Course Wavelength Division Multiplexing” (Quasi-CWDM) network, comprising steps of:
inputting a network topology, a set of service traffics between nodes in node pairs and a null route, and when selecting one of the node pairs from the set of service traffics and establishing a traffic request between the nodes in the node pair, deleting the virtual link for which the corresponding light path has no sufficient remnant capacity in an IP layer of the network topology;
finding a virtual link route having the lowest hop count in the IP layer, and determining whether each virtual link on the found route can satisfy a service request by means of traffic grooming; and
if yes, adopting a traffic grooming strategy to satisfy the service request; and
if not, adopting a wave plane based strategy to establish a light path to satisfy the service request,
wherein when adopting the wave plane based strategy to establish the light path, an extended wave plane algorithm is performed to search for the route, and a corresponding wavelength is assigned when establishing the light path between the nodes in each node pair; and wherein the adopting the wave plane based strategy to establish the light path comprises steps of:
step 1: building a set of wave planes depending on the situation of wavelength occupation for a current network link;
step 2: searching for a shortest actual route R′ between the service nodes in a pair and selecting the modulation format b′ from the set of modulation formats depending on a physical distance of the shortest actual route R′;
step 3: selecting a wave plane from the set of wave planes, searching for a route R having the shortest distance between the nodes in the pair on the wave determining whether a found shortest route R is equal to the null route, and if not, proceeding to step 4, and if yes, continuing to search for the route on a next wave plane, and if all the wave planes have been searched without finding any route R that is not equal to the null route, then blocking the service request;
step 4: depending on the physical distance of the route R found in the wave plane, selecting a modulation format b from the set of modulation formats, and if b=b′, letting a work route equal to the route R and proceeding to step 5, otherwise proceeding to the step 3 and continuing to search a next wave plane; and
step 5: determining whether the work route is equal to the null route, and if not, establishing the light path having the modulation format b along the work route and updating the set of wave planes and adding the light path to the corresponding virtual link in the IP layer, and if yes, blocking the service request.
|