| CPC H04B 17/309 (2015.01) | 18 Claims |
|
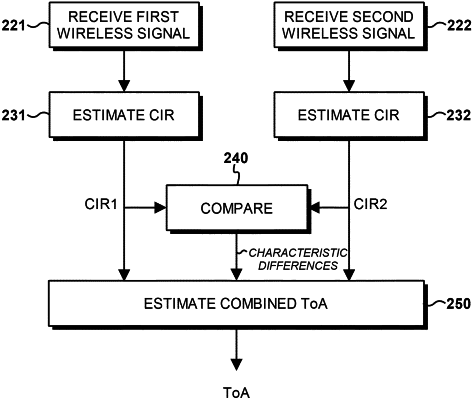
1. A method of estimating one or more characteristic differences between two wireless signals, the method comprising:
receiving a first wireless signal transmitted in a first frequency range;
receiving a second wireless signal transmitted in a second frequency range, wherein the second frequency range is spaced from the first frequency range, and wherein the second wireless signal is transmitted from the same location as the first wireless signal;
processing the first wireless signal and the second wireless signal to estimate the one or more characteristic differences between them, the one or more characteristic differences comprising at least one or any combination of two or more of:
a relative offset in their time of transmission;
a relative carrier phase relationship between them; and
a relative amplitude relationship between them; and
estimating a combined time of arrival for the first wireless signal and the second wireless signal, wherein estimating the combined time of arrival is based on the first wireless signal, the second wireless signal, and the one or more characteristic differences, and wherein estimating the combined time of arrival comprises:
aligning a first channel impulse response and a second channel impulse response, based on the one or more characteristic differences, to generate aligned channel impulse responses;
combining the aligned channel impulse responses to generate a combined channel impulse response; and
estimating the combined time of arrival from the combined channel impulse response.
|