| CPC H02P 8/12 (2013.01) [H02P 8/34 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
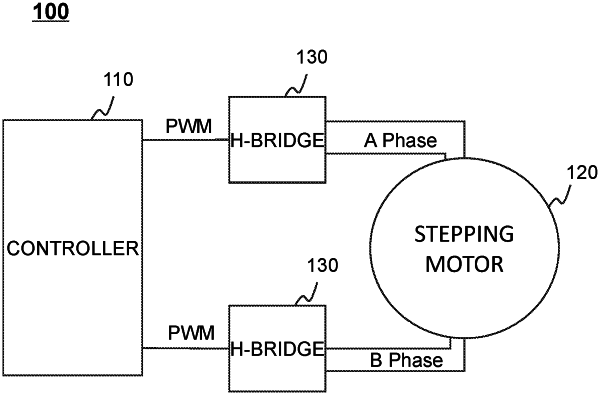
1. A system for controlling a stepping motor, comprising:
at least one storage medium including a set of instructions for controlling a stepping motor; and
at least one processor in communication with the storage medium, wherein when executing the set of instructions, the at least one processor is directed to perform operations including:
determining a driving voltage based on a function, wherein the function includes a predetermined electric current and operating parameters of the stepping motor, and the function includes |U|=√(|I|ωL+ω|C|sin γ)2+(|I|R+ω|C|cos γ)2, wherein
|U|denotes an amplitude of the driving voltage,
|I| denotes an amplitude of the predetermined electric current,
the predetermined electric current is a sinusoidal current,
ωdenotes an angular frequency of the driving voltage,
|C| denotes a back electromotive force constant of the stepping motor,
L denotes a phase inductance of the stepping motor,
γ denotes a load angle of the stepping motor, and
R denotes a sum of a phase resistance of the stepping motor and an on-resistance of the H-bridge; and
driving the stepping motor to work based on the driving voltage via an H-bridge.
|