| CPC H02J 7/00712 (2020.01) [G01R 27/08 (2013.01); H02J 7/0047 (2013.01); H02M 7/53871 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A method for recharging a vehicle battery, comprising:
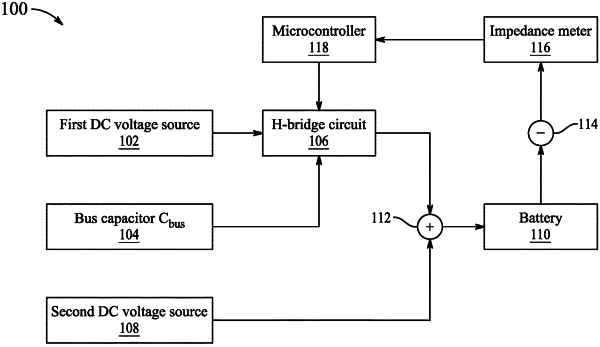
connecting a first DC voltage source to an input terminal of an H-bridge circuit, wherein the H-bridge circuit comprises four transistor switches, wherein each transistor switch includes a gate contact;
connecting a microcontroller to the gate contacts of each of the four transistor switches;
connecting an output terminal of the H-bridge circuit to a positive terminal of a rechargeable battery of a vehicle;
connecting a second DC voltage source to the positive terminal of the rechargeable battery, wherein the second DC voltage source is a lead battery;
generating, by the microcontroller, drive signals configured to control the four transistor switches;
transmitting the drive signals to the gates of each of the four transistor switches, wherein the drive signals cause the H-bridge circuit to form a sinusoidal with ripple current at the output terminal of the H-bridge circuit;
measuring, by an impedance meter connected to the microcontroller, an internal impedance of the rechargeable battery, wherein the impedance meter is connected to a negative terminal of the rechargeable battery;
performing, by the microcontroller, an autosearch algorithm to identify a frequency of the sinusoidal with ripple current at which the rechargeable battery has a minimum internal impedance by iteratively incrementing the frequency by a frequency step size which has an initial large value which is decreased after each iteration by dividing the frequency step size by two;
after each iteration, measuring, by the impedance meter, the internal impedance of the battery;
calculating, by the microcontroller, a phase value of the internal impedance after each iteration;
comparing the phase value at each step of the iteration to a phase error threshold ε;
when the phase value is less than the phase error threshold ε, identifying, by the microcontroller, the frequency as a minimum frequency at which an imaginary part of the battery impedance is zero;
measuring, by the impedance meter, a phase of a voltage at the input terminal of the battery and a phase of a current between the output terminal of the H-bridge and the input terminal of the battery at each iteration;
calculating, by the microcontroller, a phase difference between the phase of the current and the phase of the voltage;
comparing the phase difference to the phase error threshold ε;
when the phase difference is greater than the phase error threshold ε, iteratively incrementing the frequency by incrementing a previous frequency fk−1 by an amount given by: −α(512/2N), where α is a sign of the phase difference, and Nis a number of the sign changes in the phase difference from k equals one to k equals k−1, where k equals an iteration number, where N equals zero at k equals one until the phase difference is less than the phase error threshold ε;
identifying, by the microcontroller, the frequency as a minimum frequency at which an imaginary part of the battery impedance is zero;
adjusting, by the microcontroller, the drive signals to generate the sinusoidal with ripple current at the minimum frequency;
transmitting, by the microcontroller, the adjusted drive signals to the gates of each of the four transistor switches;
injecting the sinusoidal with ripple current at the minimum frequency into the rechargeable battery; and
recharging the battery with the sinusoidal with ripple current at the minimum frequency.
|