| CPC H01L 21/67051 (2013.01) [H01L 21/02057 (2013.01); H01L 21/02101 (2013.01); H01L 21/67028 (2013.01); H01L 21/67034 (2013.01); H01L 21/6715 (2013.01); H01L 21/68707 (2013.01); H01L 21/68764 (2013.01); H01L 21/6719 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A method for processing a substrate, the method comprising:
a liquid processing step for performing liquid processing on the substrate by supplying a processing liquid onto the substrate;
a drying step for drying the substrate after the liquid processing step; and
a transfer step for transferring the substrate from a liquid processing chamber to a drying chamber after the liquid processing step,
wherein the liquid processing step is performed in the liquid processing chamber and the drying step is performed in the drying chamber,
wherein the liquid processing step comprises:
a liquid supply step for supplying the processing liquid toward the substrate; and
a liquid level adjustment step for rotating the substrate after the liquid supply step,
wherein the substrate is rotated at a first speed in the liquid supply step and at a second speed in the liquid level adjustment step, and the second speed is different from the first speed,
wherein the liquid supply step comprises:
a first supply step for rotating the substrate and supplying the processing liquid toward a central region of the substrate; and
a second supply step for rotating the substrate and supplying the processing liquid onto an edge region of the substrate after the first supply step,
wherein the first supply step, the processing liquid is supplied by a nozzle from above the central region of the substrate, and
wherein the second supply step, the processing liquid is supplied by the nozzle from above the edge region of the substrate,
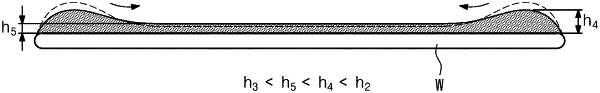
wherein the substrate is transferred from the liquid processing chamber to the drying chamber, such that in the transfer step, a height of the processing liquid on two edge regions of the substrate are both higher than a height of the processing liquid on the central region of the substrate, wherein the two edge regions are on opposite sides of the central region.
|