| CPC G09G 5/005 (2013.01) [G06T 1/20 (2013.01); G09G 5/001 (2013.01); G09G 5/363 (2013.01); G09G 5/38 (2013.01); G09G 5/391 (2013.01); G09G 2360/06 (2013.01); G09G 2360/08 (2013.01); G09G 2360/121 (2013.01); G09G 2360/125 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
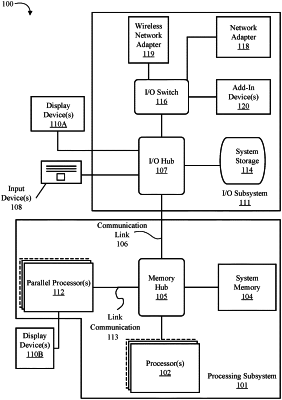
1. An apparatus comprising:
a memory interface; and
a graphics processing unit coupled to the memory interface, the graphics processing unit to:
assign a first rate to a first region of a frame; and
assign a second rate to a second region of the frame, wherein the second rate indicates a greater number of pixels to share a pixel shader result than the first rate, wherein the first rate and the second rate are selected in response to identified motion, wherein the identified motion is based on temporal anti-aliasing data, and wherein the second region corresponds to higher motion content than the first region based on the identified motion from the temporal anti-aliasing data.
|