| CPC G06F 21/56 (2013.01) [H04L 2463/144 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
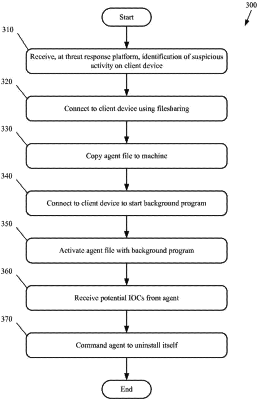
1. A method for threat detection and response, the method comprising:
receiving, by a threat response computer, an event report from a threat detector which monitors and analyzes communications between a client computer in an enterprise computing network and a plurality of computers, wherein the threat response computer is separate from the client computer and runs on a threat response platform configured for protecting the enterprise computing network, and wherein the event report includes data identifying a suspicious communication by the client computer as a security event;
in response to the receiving of the event report by the threat response computer, temporarily, automatically, and remotely placing and activating, by the threat response computer, an agent on the client computer, the agent configured to search for potential indications of compromise (IOCs) on the client computer and self-uninstall after sending search result data to the threat response computer;
determining, by the threat response computer, whether the potential IOCs on the client computer indicate evidence of malware on the client computer in the enterprise computing network by:
comparing the potential IOCs on the client computer in the enterprise computing network and IOCs in a database local to the threat response computer, and
using a result of the comparison of the potential IOCs on the client computer in the enterprise computing network with the IOCs in the database local to the threat response computer, determining a probability of an actual malware incursion on the client computer; and
responsive to a result of the determining whether the potential IOCs on the client computer indicate evidence of malware on the client computer comprising a determination that the potential IOCs on the client computer indicate the evidence of malware on the client computer in the enterprise computing network, performing, by the threat response computer, one or more of:
updating the database local to the threat response computer to include the evidence of malware determined by the threat response computer, or
sending an instruction from the threat response computer to configure a firewall in the enterprise computing network.
|