| CPC G01V 1/34 (2013.01) [G01V 1/30 (2013.01); G06N 3/045 (2023.01); G06N 3/088 (2013.01); G01V 2210/1295 (2013.01); G01V 2210/1425 (2013.01); G01V 2210/32 (2013.01); G01V 2210/64 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
10. A method, comprising:
obtaining, by a computer processor, a first machine-learning model comprising an encoder model and a decoder model;
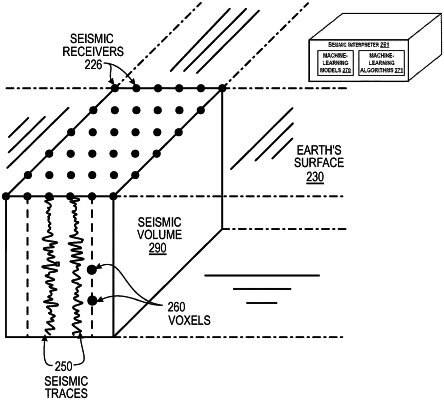
obtaining, by the computer processor, a plurality of input gathers based on a seismic processing operation,
wherein the plurality of input gathers comprise seismic data acquired from one or more seismic surveys, and
wherein the seismic processing operation performs one or more demultiple functions for removing at least one surface multiple from the seismic data;
obtaining, by the computer processor, first parameterization data for the seismic processing operation;
generating, by the computer processor, a first plurality of predicted output gathers using the first machine-learning model, the plurality of input gathers, and the first parameterization data;
updating, by the computer processor, the first machine-learning model using a first machine-learning algorithm and error data to produce a first trained model,
wherein the error data describes a mismatch between the first plurality of predicted output gathers and the plurality of input gathers;
obtaining, by the computer processor, an input gather regarding a geological region of interest;
generating, by the computer processor, a predicted output gather using the first trained model, the input gather, and second parameterization data for the seismic processing operation;
obtaining, by the computer processor, a second machine-learning model, wherein the second machine-learning model is pre-trained to predict migrated seismic data;
selecting, by the computer processor, a plurality of training gathers based on a portion of a second plurality of predicted output gathers comprising the predicted output gather, a migration function, and a velocity model;
generating, by the computer processor, a second trained model using the plurality of training gathers, the second machine-learning model, and a second machine-learning algorithm;
generating, by the computer processor, a seismic image of the geological region of interest using the second trained model and a remaining portion of the second plurality of predicted output gathers,
wherein the seismic image comprises depth data that describes one or more subsurface formations in the geological region of interest; and
determining, by the computer processor, a predicted hydrocarbon deposit in the geological region of interest based on the one or more subsurface formations in the seismic image.
|