| CPC F01N 11/007 (2013.01) [F01N 11/00 (2013.01); F01N 2550/02 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
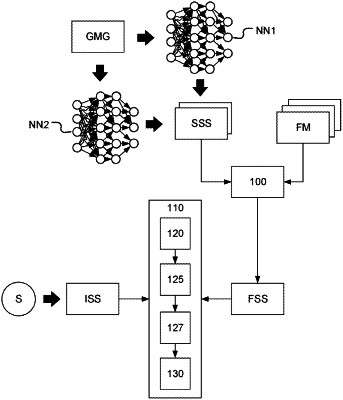
|
1. A method for identifying a sensor fault of a sensor for an exhaust-gas system of a motor vehicle, the method comprising the steps of:
determining at least one actual sensor signal of the sensor;
determining at least one setpoint sensor signal of the sensor by way of at least one fault model; and
identifying the sensor fault of the sensor in a manner dependent on a deviation between the actual sensor signal of the sensor and the setpoint sensor signal of the sensor, wherein the at least one fault model comprises at least one of the following fault models:
(i) time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture, and no time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture,
(ii) time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture, and no time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture,
(iii) low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture, and no low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture,
(iv) low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture, and no low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture,
(v) time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture, and time delay of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture, or
(vi) low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a lean mixture to a rich mixture, and low-pass filtering of the actual sensor signal relative to the setpoint sensor signal in the event of a change of the combustion air ratio from a rich mixture to a lean mixture.
|