| CPC A61B 17/12036 (2013.01) [A61B 17/12031 (2013.01); A61B 17/12136 (2013.01); A61M 25/10185 (2013.11); A61B 2562/0247 (2013.01); A61M 2025/0008 (2013.01); A61M 2025/1004 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. An occlusion catheter system for full or partial occlusion of an aorta having an inner diameter, the occlusion catheter system comprising:
a proximal catheter shaft having a proximal lumen;
a central shaft positioned partially within the proximal lumen and spaced from the proximal catheter shaft;
a distal catheter shaft attached to a distal end of the central shaft; and
an occlusion balloon having a proximal end and a distal end, the occlusion balloon connected at the proximal end to the proximal catheter shaft and at the distal end to the distal catheter shaft, the occlusion balloon being positioned in a folded, uninflated configuration around the central shaft, the proximal catheter shaft, the distal catheter shaft and the occlusion balloon in the folded configuration having an outer diameter less than seven French, and
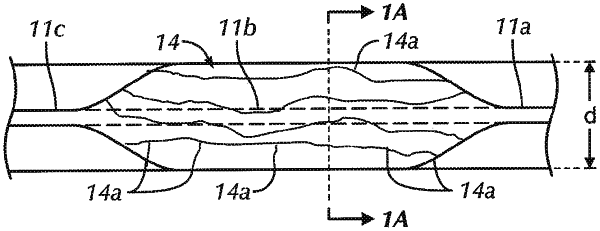
the occlusion balloon being constructed of a semi-compliant or non-compliant material and sized to have a blown diameter between approximately ten percent to sixty percent greater than the inner diameter of the aorta, whereby an outer surface of the occlusion balloon comes into diametric contact with an inner surface of the aorta upon partial inflation of the occlusion balloon and folds are formed in the outer surface of the occlusion balloon, the folds defining flow channels with inner surfaces of the aorta or with portions of the outer surface of the occlusion balloon that allow partial blood flow past the occlusion balloon.
|