| CPC H04Q 11/0062 (2013.01) [H04B 10/038 (2013.01); H04B 10/0795 (2013.01); H04B 10/07953 (2013.01); H04Q 2011/0081 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
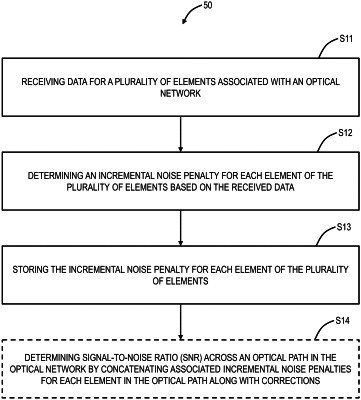
1. A non-transitory computer-readable medium comprising instructions that, when executed, cause one or more processors to perform steps of:
receiving data for a plurality of elements associated with an optical network and receiving calibration data associated with one or more of the plurality of elements, the received calibration data is received via a northbound interface;
determining an incremental noise penalty for each element of the plurality of elements based on the received data and the received calibration data; and
storing the incremental noise penalty for each element of the plurality of elements.
|