| CPC H02J 4/00 (2013.01) [B60L 50/51 (2019.02); H02H 3/165 (2013.01); B60L 2200/10 (2013.01); B60L 2210/40 (2013.01); B64D 2045/0085 (2013.01); B64D 2221/00 (2013.01); H02J 2310/44 (2020.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
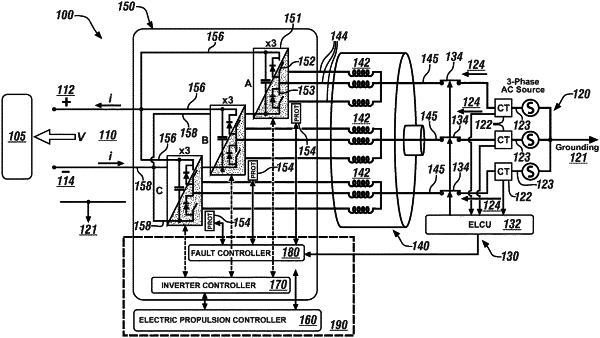
1. An electrical system for an aircraft, comprising:
a polyphase AC electric power source electrically connected to a polyphase rotary electric motor via a plurality of AC contactors;
an AC/DC inverter electrically connected to the polyphase rotary electric motor;
a DC power bus electrically connected to the AC/DC inverter;
a plurality of sensors arranged to monitor a plurality of electric currents between the polyphase AC electric power source and the polyphase rotary electric motor;
a first controller arranged to control the AC/DC inverter; and
a second controller arranged to monitor the plurality of sensors and operatively connected to the plurality of AC contactors;
wherein the second controller is operable to:
monitor, via the plurality of sensors, the plurality of electric currents between the polyphase AC electric power source and the polyphase rotary electric motor;
detect a fault based upon the plurality of electric currents; and
deactivate the plurality of AC contactors in response to the fault.
|