| CPC G16H 50/70 (2018.01) [G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. An emergency medical service demand prediction device that predicts a quantity of occurrences of emergency medical service requests in a target area, the emergency medical service demand prediction device comprising:
a memory configured to store computer program instructions; and
a processor configured to execute the computer program instructions so as to:
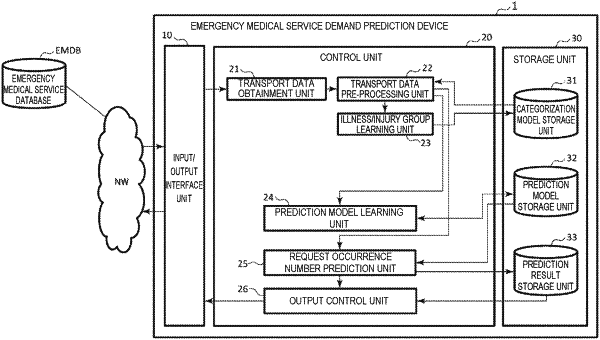
obtain actual history data including transport data from an external emergency medical service database, information transmitted from ambulances currently responding to the emergency medical service requests, date/time information indicating dates and times of occurrences of the emergency medical service requests, position information indicating places of the occurrences of the emergency medical service requests, illness/injury information indicating illnesses and injuries that caused the emergency medical service requests, and attribute information of patients including ages and genders;
pre-process the actual history data by dividing the actual history data into sections, extracting related items, and performing a normalization process to generate:
illness/injury group learning-purpose data used for learning the illnesses and injuries;
prediction model learning-purpose data used for learning a prediction model based on an actual number of the occurrences, the date/time information of each of the illnesses and injuries, and the position information; and
request occurrence number prediction-purpose data used for predicting a quantity of occurrences of future emergency medical service requests;
generate a first learning model, based on the illness/injury group learning-purpose data, including illness/injury groups in which the illnesses and injuries are grouped by a type of the illnesses and injuries by learning occurrence patterns of the illnesses and injuries, and similarities or distances among the illnesses and injuries in association with the dates and times, the position information, and the attribute information of the patients;
generate a second learning model, based on the first leaning model and the prediction model learning-purpose data, including a learned prediction model in which a relationship among a number of occurrences of the illnesses and injuries, the illness/injury groups, the dates and times, and the position information are learned, the learned prediction model indicating an actual number of the occurrences of the emergency medical service requests by the illness/injury groups, unit time, and unit areas in the position information;
predict the quantity of the occurrences of the future emergency medical service requests in each of the unit areas within the target area based on the second learning model and the request occurrence number prediction-purpose data; and
output the predicted quantity of the occurrences of the future emergency medical service requests to an external device.
|