| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G06T 2207/20 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30028 (2013.01)] | 1 Claim |
|
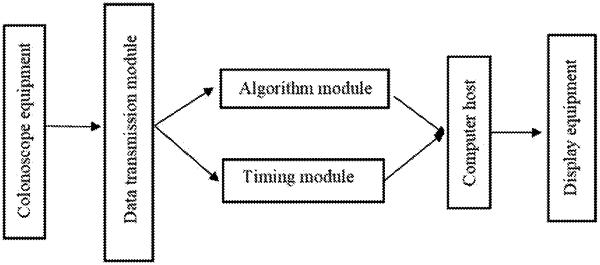
1. An image recognition based workstation for evaluation on quality check of colonoscopy, comprising: an algorithm module, a timing module, a data transmission module, display equipment, colonoscope equipment and a computer host,
wherein the colonoscope equipment is connected to the data transmission module, the data transmission module is connected to the computer host by means of the algorithm module and the timing module, the display equipment is configured to display a result of the computer host, and
the algorithm module comprises a fuzzy detection algorithm, an examination completeness degree algorithm, a lesion recognition algorithm, a static detection algorithm and a wall collision detection algorithm,
wherein the fuzzy detection algorithm uses a function in opencv to gray an input image to obtain a grayed input image, uses a laplace operator to detect a global variance of the grayed input image, and conducts marginal detection on the grayed input image, so that the global variance of the grayed input image is calculated, and first threshold value is determined so as to determine whether the grayed input image is fuzzy or not; the examination completeness degree algorithm is used to detect an average gray value of part of areas of four corners in the grayed input image and select second threshold value to determine whether the four corners are bright or dark, and under a condition that brightness of each corner in a certain number of image dead angles continuously input is included,
an examination is complete, and otherwise, the examination is incomplete; the lesion recognition algorithm uses a YOLO V3 algorithm, and can detect a position of a lesion in an input video image in real time; the static detection algorithm is used to calculate a gray histogram of two images spaced a certain number of frames apart, and when a matching degree reaches a certain threshold value, it is determined that a colonoscope lens is in a static state within time corresponding to the number of frames; the wall collision detection algorithm trains a collected picture that is too close to an intestinal wall through a deep learning method, so as to obtain a detection model; and the timing module is used to calculate total examination time and colonoscope withdrawal time.
|