| CPC G06F 3/0613 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0653 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01); G06F 12/0246 (2013.01); G06N 3/0442 (2023.01); G06F 2212/7211 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
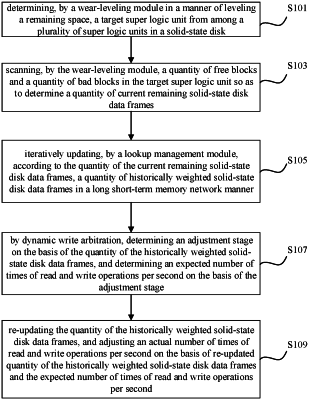
1. A random write method, comprising:
determining, in a manner of leveling a remaining space, a target super logic unit from among a plurality of super logic units in a solid-state disk;
scanning a quantity of free blocks and a quantity of bad blocks in the target super logic unit so as to determine a quantity of current remaining solid-state disk data frames;
iteratively updating a quantity of historically weighted solid-state disk data frames in a long short-term memory network manner according to the quantity of the current remaining solid-state disk data frames;
by dynamic write arbitration, determining an adjustment stage on the basis of the quantity of the historically weighted solid-state disk data frames, and determining an expected number of times of read and write operations per second on the basis of the adjustment stage;
re-updating the quantity of the historically weighted solid-state disk data frames, and adjusting an actual number of times of read and write operations per second on the basis of re-updated quantity of the historically weighted solid-state disk data frames and the expected number of times of read and write operations per second;
wherein the dynamic write arbitration comprises three stages, each stage comprises a corresponding relationship between the quantity of the free blocks, the quantity of the historically weighted solid-state disk data frames, and the number of times of read and write operations per second.
|