| CPC G06F 16/35 (2019.01) [G06F 11/3409 (2013.01); G06F 16/24568 (2019.01); G06F 16/9024 (2019.01); G06F 16/9535 (2019.01); G06Q 30/0201 (2013.01); G06Q 50/01 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
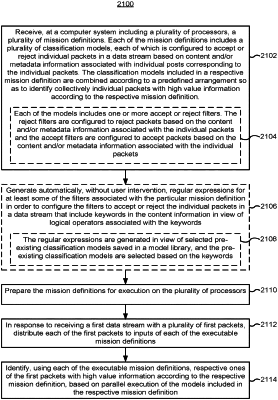
1. A method for identification of high-value information in data streams, comprising:
at a computer system including a plurality of processors and memory storing programs for execution by the processors:
receiving a plurality of filter graphs, each filter graph including a plurality of filter nodes interrelated by a plurality of graph edges, each filter node representing a classification model;
performing a continuous monitoring process for a data stream that includes a plurality of data packets from a plurality of sources, including:
without user intervention, in response to receiving the data stream with the plurality of data packets, distributing the plurality of data packets to inputs of the plurality of filter graphs; and
identifying whether each of the plurality of data packets includes high-value information related to a particular concept with regard to the respective filter graphs, based on parallel execution of the filter nodes included in the respective filter graphs, by applying predefined criteria associated with the particular concept with respect to classification models of corresponding filter nodes to text content and author information associated with the plurality of data packets;
wherein applying the predefined criteria to the text content and the author information of each data packet of the plurality of data packets includes:
executing one or more textual filters on the text content of the data packets and one or more author filters on the author information of the data packets in accordance with a first of the classification models; and
determining whether to tag each of the plurality of data packets with an identifier of the first classification model or to tag each of the plurality of data packets as rejected with the identifier of the first classification model based on whether each of the plurality of data packets is accepted by the first classification model;
upon determining that at least one of the plurality of data packets includes high-value information related to the particular concept, generating statistical information related to the high-value information; and
upon determining that the statistical information meets or exceeds a predetermined threshold, triggering an alarm, including sending a notification to a designated recipient indicating that the predetermined threshold has been met or exceeded.
|