| CPC G02F 1/167 (2013.01) [G02F 1/1675 (2019.01); G02F 1/16755 (2019.01); G02F 1/16756 (2019.01); G02F 1/1676 (2019.01); G02F 1/1685 (2019.01); G09F 9/37 (2013.01); G09F 9/375 (2013.01); G02F 2201/50 (2013.01); G02F 2202/10 (2013.01)] | 33 Claims |
|
1. A light modulator comprising:
a first substrate and a second substrate, the first and second substrates being arranged with inner sides opposite to each other,
multiple electrodes being applied to the inner side of each of the first and second substrates, each of the first and second substrates having an inner surface area,
wherein each of the multiple electrodes is arranged in a pattern across the substrate, the multiple electrodes each comprising a multiple of main-lines extending across the substrate in a first direction, the multiple of main-lines of the multiple electrodes being arranged alternatingly with respect to each other on the substrate, and
wherein at least a part of the inner surface area of at least one of the first substrate and the second substrate is provided with a protective coating to protect the electrodes;
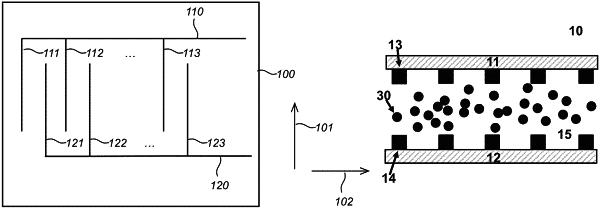
an optical layer between the first and second substrates, the optical layer comprising a fluid comprising particles, wherein the particles are electrically charged or chargeable;
a controller configured to apply an electric potential to the multiple electrodes to obtain an electro-magnetic field between the multiple electrodes providing electrophoretic movement of the particles towards or from one of the multiple electrodes causing modulation of the optical properties of the light modulator, wherein the multiple electrodes of at least one of each substrate comprise at least a first electrode and a second electrode, the first electrode and the second electrode each comprising:
a multiple of main-lines extending across the substrate in a first direction, the multiple of main-lines of the first and second electrode being arranged alternatingly with respect to each other on the substrate;
multiple branches extending from the main-lines into the areas between the main-lines, the branches that extend into an area between a first main-line and a second main-line of the first electrode and of the second electrode extending alternatingly from the first and second main-line, at least one of two subsequent branches that extend into the same area extending at least half across the area, measured along a second direction orthogonal to the first direction, wherein two subsequent branches that extend into the same area between a first main-line and a second main-line overlap in the second direction when projected in the first direction.
|