| CPC G01N 1/04 (2013.01) [C04B 14/361 (2013.01); C04B 28/04 (2013.01); E04B 2/18 (2013.01); E04C 1/00 (2013.01); G01N 33/24 (2013.01); G01N 3/08 (2013.01); G01N 3/20 (2013.01); G01N 2203/0003 (2013.01); G01N 2203/0019 (2013.01); G01N 2203/0023 (2013.01); G01N 2203/0067 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A method of determining a soil classification for selecting a soil additive comprising:
obtaining a soil sample;
conducting two or more field tests on the soil sample to determine percent gravel, percent fines, and the plasticity index to obtain raw data for each of the two or more field tests, wherein at least one test is qualitative and one test if quantitative, wherein the qualitative field test is selected from at least one of pen, stick, and shine tests, and the quantitative test is selected from at least one of a wash test, a feel test, a test tube particle graduation, or a jar test;
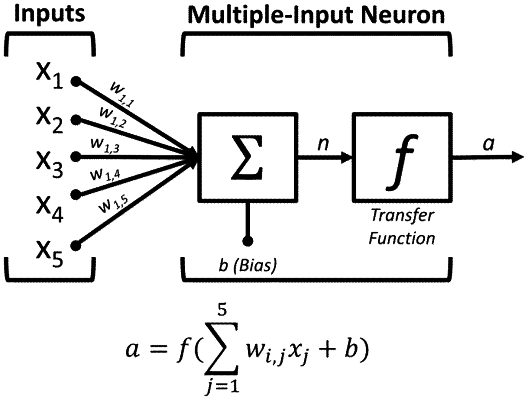
using a processor to train a neural network using at least two hidden layers to obtain a validation dataset that is applied to the soil sample tests of both quantitative and qualitative datasets; and
calculating the soil classification from the raw data by applying the validation dataset obtained from a training and validation soil classification calculation of both quantitative and qualitative datasets using samples of known soil classification, wherein the validation dataset is obtained using a feed-forward backpropagation neural network, wherein the training occurs by adjustment of one or more synaptic weights, wherein the one or more synaptic weights are initialized as random numbers in a first pass of a training dataset that are input into the feed-forward backpropagation neural network and an output is generated, if this output does not match a target output within a predefined acceptable error, the weights and biases within the feed-forward backpropagation neural network are adjusted by reducing an error function related to a simulated output and the target output; and
wherein the soil classification is within 10% of a known soil classification obtained using laboratory testing of a soil having any known soil classification;
wherein the soil classification is used for selecting the soil additive used to prepare a mix for making a compressed earth block brick of a desired brick strength.
|