| CPC C12N 15/87 (2013.01) [A61N 1/08 (2013.01); C12M 35/02 (2013.01); A61N 1/0476 (2013.01); A61N 1/378 (2013.01); H03K 3/00 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
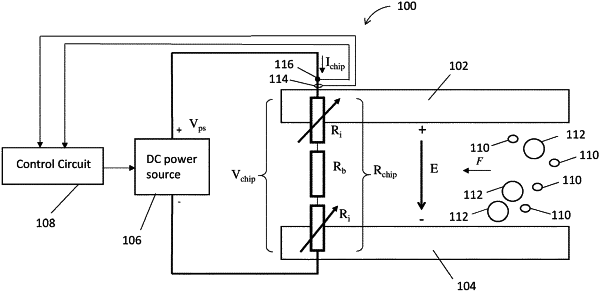
1. An apparatus for electroporating cells with a cargo, the apparatus comprising:
two electrodes spaced apart from each other and defining a path for a fluid including the cells and the cargo to flow therebetween, the electrodes having a resistance therebetween when fluid flows through the path;
a DC power source coupled across the electrodes; and
a control circuit configured to control the DC power source to provide a plurality of electrical pulses at a voltage to the electrodes to induce a current through the electrodes for generating an electric field between the electrodes at a defined value, detect a decrease in the induced current due to an increase in the resistance between the electrodes, determine at least a first value and a second value of the resistance between the electrodes over a period of time, apply a linear projection between the first value of the resistance and the second value of the resistance, predict a future value of the resistance between the electrodes based on the linear projection, and control the DC power source to increase the induced current based on the future value of the resistance to maintain the electric field between the electrodes at the defined value.
|
|
12. A method of electroporating cells with a cargo, the method comprising:
flowing a fluid including the cells and the cargo in a path defined by two electrodes spaced apart from each other, the electrodes having a resistance therebetween when fluid flows through the path;
controlling a DC power source to provide a plurality of electrical pulses at a voltage to the electrodes to induce a current through the electrodes to generate an electric field between the electrodes at a defined value;
detecting a decrease in the induced current due to an increase in the resistance between the electrodes;
determining at least a first value and a second value of the resistance between the electrodes over a period of time;
applying a linear projection between the first value of the resistance and the second value of the resistance;
predicting a future value of the resistance between the electrodes based on the linear projection; and
controlling the DC power source to increase the induced current based on the future value of the resistance to maintain the electric field between the electrodes at the defined value.
|