| CPC B64C 29/0033 (2013.01) [B60L 50/66 (2019.02); B64C 21/04 (2013.01); B64C 25/04 (2013.01); B64C 39/08 (2013.01); B64D 27/18 (2013.01); B64D 27/24 (2013.01); B60L 2200/10 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
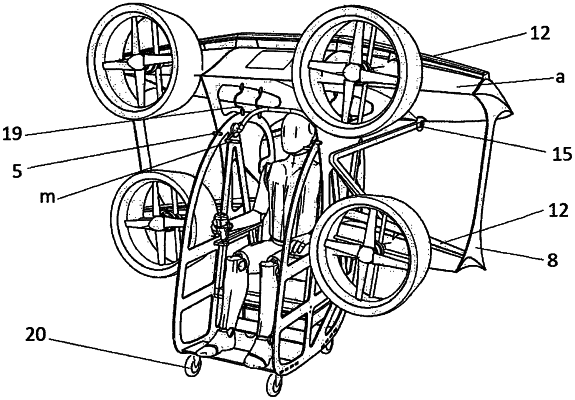
1. Flight apparatus with vertical take-off and landing, of a biplane type, having two main distinct parts which are articulated between them, a first distinct part consisting of a cockpit hinged to a second distinct part which is a wings assembly; the cockpit being attached to the wings assembly by two hinges fixed in upright central vertical supports of an upper wing and a lower wing b, wherein the upper wing a and the lower wing b are provided with four propellers driven by four electric engines, two of the four propellers being disposed on the upper wing a and two of the four propellers on the lower wing b, the four propellers forming thus a quadcopter layout;
wherein each of the four propellers has a duct;
wherein batteries transmit electric energy to the four electric engines through speed regulators and the batteries are placed under a pilot's seat;
wherein the entire operation of the flight apparatus is managed by means of a flight computer which is disposed in a central part of the upper wing a;
wherein the taking-off is made with the wings a and b and the four electric engines vertically oriented;
wherein the flight apparatus is supported on the ground by means of a landing gear fixed in the extremities of the upper wing a and the lower wing b;
wherein the flight apparatus taking off as a quadcopter and the transition to a cruise flight is made by reducing an angle of incidence of the upper wing a and lower wing b, wherein the angle of incidence decreases naturally due to the increasing drag on the upper wing a and the lower wing b, concurrently with an increasing of the translation speed of the flight apparatus, in the meantime, the cockpit remaining in a vertical orientation due to the cockpit's lower center of gravity and due to the two hinges which allow the cockpit to rotate relative to the wings assembly;
and wherein a landing is made similarly to a quadcopter, slowing down the translation speed in order to lead an increasing of the angle of incidence of the wings a and b until the wings a and b naturally return to the vertical position required for landing, wherein
the lower wing b is discontinuous and consists of a left side and a right side, which are physically separated by an open space situated between the upright central vertical supports and inner edges of the left and right side of lower wing b, and the cockpit rotates between the left side and right side within the open space of the lower wing b;
the cockpit has a lower center of gravity relative to the hinges thus determining the cockpit to naturally remain in the vertical orientation in all the phases of flight;
the hinges are configured to permit the cockpit to rotate with respect to the wings assembly, with a limited arc of rotation of the cockpit; and
the cockpit's center of gravity naturally shifts forward relative to the wings assembly.
|