| CPC B61L 27/53 (2022.01) [B61L 1/02 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
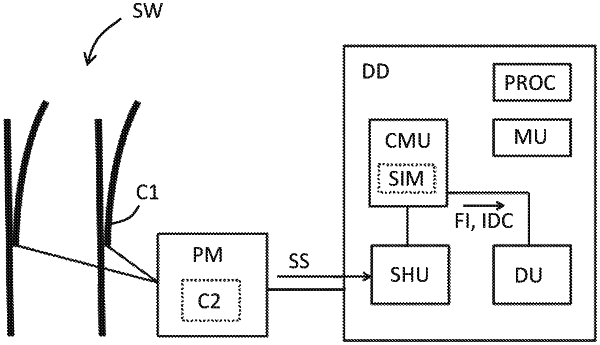
1. A computer-implemented method for diagnosing a railroad switch with a point machine, the method comprising:
a) receiving a first time series and a second time series of a sensor signal of the point machine, the sensor signal being sensitive to an operation of the point machine;
b) detecting changes in the first time series and the second time series indicating changes of operational conditions of the point machine;
c) allocating an event point of a respective change in the first time series and in the second time series to a respective component of the railroad switch or of the point machine based on a simulation modelling the respective component; and
d) for a respective component:
identifying event points allocated to the respective component;
comparing the sensor signal at a first identified event point in the first time series with the sensor signal at a second identified event point in the second time series; and
depending on the comparing, outputting a component-specific fault information and an identification of the respective component
wherein, at least one of:
(1) a mismatch between the sensor signal at the first identified event point and the sensor signal at the second identified event point is quantified, and from the quantified mismatch a quantified fault information is derived and output; and
(2) a dynamic time warping method is used to quantify a measure of a similarity between the first time series and the second time series, and from the quantified similarity measure a quantified fault in-formation is derived and output,
wherein at least one of the quantified mismatch and the quantified similarity is compared with a predetermined threshold to determine whether the respective component is damaged or not.
|