| CPC B25J 9/0006 (2013.01) [G06F 3/015 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01)] | 20 Claims |
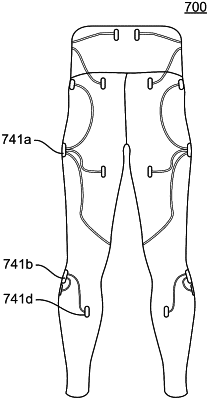
|
1. A method comprising:
monitoring a plurality of movement signals representative of movement of a user;
identifying, using a machine-learned model configured to determine an intended movement by the user based on motor intent data received from the user, a difference between the plurality of movement signals and a plurality of target movement signals representative of the intended movement;
determining a plurality of actuation signals based on the identified difference;
applying the plurality of actuation signals to one or more augmentation devices worn by the user, the application of the plurality of actuation signals causing an actuated movement of the user;
updating the plurality of actuation signals based on the actuated movement of the user and the intended movement; and
applying the updated actuation signals to the one or more augmentation devices worn by the user, the application of the updated actuation signals configured to minimize a difference between subsequently monitored movement signals and the plurality of target movement signals.
|