| CPC B22F 10/14 (2021.01) [B22F 10/30 (2021.01); B22F 10/64 (2021.01); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 30/00 (2014.12); B33Y 80/00 (2014.12); B22F 2203/11 (2013.01); B22F 2304/10 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
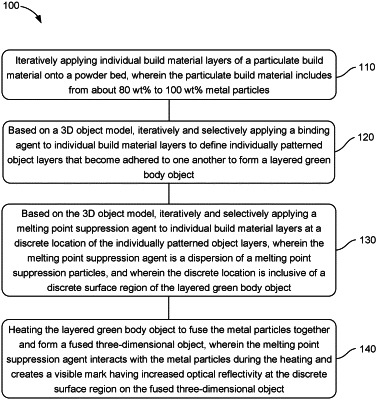
1. A method of three-dimensional printing comprising:
iteratively applying individual build material layers of a particulate build material onto a powder bed, wherein the particulate build material includes from about 80 wt % to 100 wt % metal particles;
based on a 3D object model, iteratively and selectively applying a binding agent to individual build material layers to define individually patterned object layers that become adhered to one another to form a layered green body object;
based on the 3D object model, iteratively and selectively applying a melting point suppression agent to individual build material layers at a discrete location of the individually patterned object layers, wherein the melting point suppression agent is a dispersion of a melting point suppression particles, and wherein the discrete location is inclusive of a discrete surface region of the layered green body object; and
heating the layered green body object to fuse the metal particles together to form a fused three-dimensional object, wherein the melting point suppression agent interacts with the metal particles during the heating and creates a visible mark having increased optical reflectivity at the discrete surface region on the fused three-dimensional object.
|