| CPC A61F 9/00781 (2013.01) | 20 Claims |
|
1. A device for the treatment of excess fluid pressure within an eye, the device comprising:
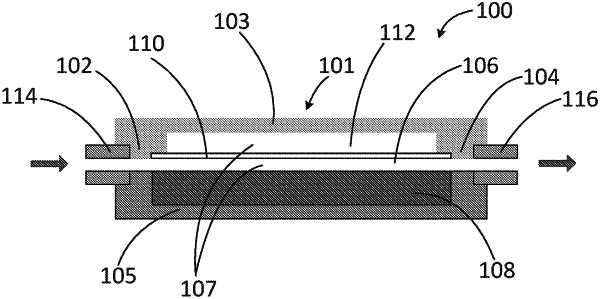
a housing shell configured to be implanted beneath a conjunctiva, the housing shell having a first end configured for fluid communication with an anterior chamber of the eye, a second end configured for fluid communication with a space beneath tissue of the eye, and defining a cavity between the first end and the second end, the cavity having a circular-shaped cross-section;
an elastic membrane disposed within the cavity to define a fluidic channel that permits a flow of fluid from the first end to the second end, the elastic membrane configured to seal off the fluidic channel and deform to change the volume of the fluidic channel directly responsive to pressure fluctuations between the first and second ends, thereby varying the fluidic resistance of the flow of fluid through the fluidic channel to maintain pressure at the first end relatively constant; and
a local constriction disposed within a center of the housing shell, coaxial with the cavity and extending along an entire length of the fluidic channel to reduce the area of the fluidic channel to increase fluidic resistance of the flow of fluid through the fluidic channel, an outer surface of the local constriction comprising one or more grooves,
wherein the elastic membrane requires a predetermined level of force to deform is, and change the area of the fluidic channel.
|