| CPC A61B 5/0044 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02007 (2013.01); G16B 40/20 (2019.02); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/50 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); A61B 5/026 (2013.01); G16B 45/00 (2019.02)] | 20 Claims |
|
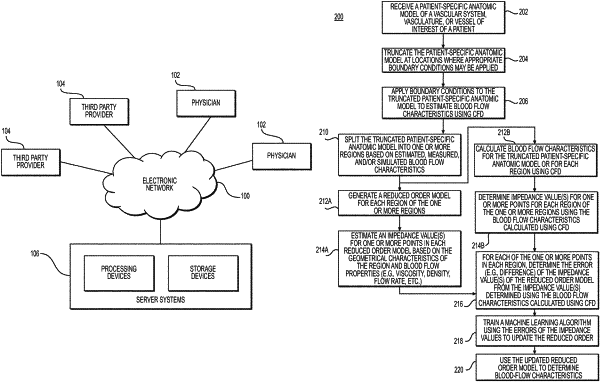
1. A computer-implemented method of determining blood flow characteristics of a patient, the method comprising:
obtaining a reduced-order model that is representative of at least a portion of a patient-specific anatomic model of at least a portion of a patient's vasculature, the reduced-order model including one or more points having an impedance value based on first estimated values of blood flow characteristics at one or more locations of the portion of the patient-specific anatomic model;
updating the reduced-order model by employing a machine-learning algorithm that has been trained, based on errors determined between at least one impedance value of at least one training reduced-order model and at least one corresponding impedance value determined by computational fluid dynamics, to reduce error in one or more impedance values of an input reduced-order model; and
using the updated reduced-order model to determine second estimated values for the blood flow characteristic at the one or more locations of the portion of the patient-specific anatomic model.
|