| CPC H04L 67/10 (2013.01) [G10L 15/1815 (2013.01); G10L 25/72 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
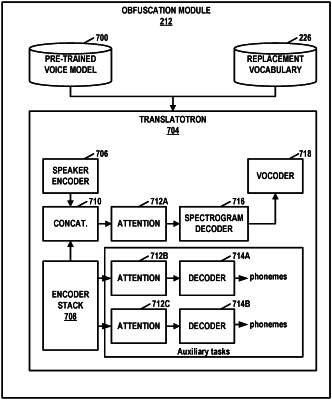
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
obtaining, by one or more processors of a first computing system, first audio data representing one or more initial utterances during an interactive voice session with an interactive voice system that interacts with a server to obtain content to provide to a user during the interactive voice session, wherein the interactive voice system is configured to execute on a second computing system and the server is configured to execute on a third computing system;
transmitting, by the one or more processors of the first computing system, the first audio data to the interactive voice system via a first communication channel;
generating, by the one or more processors of the first computing system, based on the first audio data, a prediction that a second audio data representing a subsequent utterance of the user in the interactive voice session will contain sensitive information, wherein the subsequent utterance follows the one or more initial utterances in time;
upon obtaining, by the one or more processors of the first computing system, the second audio data that includes the sensitive information:
transmitting, by the one or more processors of the first computing system, third audio data to the interactive voice system via the first communication channel in place of the second audio data, wherein the third audio data represents data that replaces the sensitive information; and
transmitting, by the one or more processors of the first computing system, the second audio data to the server via a second communication channel that bypasses the interactive voice system.
|