| CPC H04L 41/147 (2013.01) [H04L 43/0811 (2013.01); H04L 47/125 (2013.01); H04L 47/76 (2013.01); H04L 67/60 (2022.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
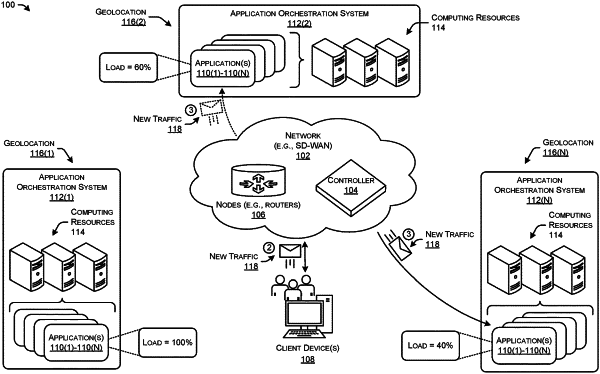
receiving, from a client device and at a controller of a network, a request to route traffic through the network between the client device and an application;
receiving, at the controller, load information associated with different instances of the application hosted in different cloud-service provider zones, the load information including at least:
first load information associated with a first instance of the application hosted in a first cloud-service provider zone, the first cloud-service provider zone including first scalable resources for hosting the first instance of the application; and
second load information associated with a second instance of the application hosted in a second cloud-service provider zone, the second cloud-service provider zone including second scalable resources for hosting the second instance of the application;
determining, by the controller and based at least in part on the load information, that the first instance of the application is less constrained than the second instance of the application; and
based at least in part on the first instance of the application being less constrained than the second instance of the application, causing, by the controller, one or more network nodes of the network to forward the traffic through the network to the first instance of the application hosted in the first cloud-service provider zone.
|